The Importance of Chemical Resistant Gloves: Protecting Your Hands in Hazardous Environments
Chemical resistant gloves keep hands safe from harmful chemicals at work. Workers can get burns, skin problems, or health issues from dangerous substances.
• In 2014, there were over 1.1 million hand injuries in the U.S.
• More than 70% of hurt workers did not wear gloves.
• 30% wore gloves, but they were not the right kind.
More chemical accidents have led to stricter safety rules and better glove designs. Companies now use new gloves, like INTCO’s ChemTuff™ Disposable Nitrile Gloves, for more safety and comfort.
Why Chemical Resistant Gloves Matter
Risks of Chemical Exposure
Chemicals can hurt your skin and body in many ways. People who work with chemicals can get burns or rashes. They might also have health problems that last a long time. A study from PMC says pesticides and other chemicals can cause skin rashes and breathing trouble. Some chemicals can even lead to cancer or nerve problems. The study says chemicals can build up in your body over time. This can cause health problems that do not show up right away. For example, some chemicals can mess with hormones or hurt the heart and reproductive system after many years.
Frontiers research uses health risk tests to check these dangers. These tests, like COSHH and CHEM-SAM, help experts see how likely burns or skin cancer are. Workers on drilling rigs who are exposed to chemicals for a long time have a higher risk of skin cancer. These studies show chemical exposure is not just a quick problem. It can hurt your health for a long time.
• Note: Even a little chemical exposure can add up over time. Workers should always wear the right protection to stay safe.
Role in Workplace Safety
Chemical Resistant Gloves help keep workers safe at their jobs. These gloves make a barrier between your skin and dangerous chemicals. Wearing the right gloves lowers the chance of burns or rashes. Safety experts use risk tests to pick the best gloves for each job. This makes sure workers get the best safety.
Many places like factories, labs, and food plants need Chemical Resistant Gloves. These gloves help stop accidents and keep workers healthy. Companies that use the right gloves have fewer injuries and spend less on health care. Workers feel safer and more secure when their hands are protected.
Wearing the right gloves is a big part of staying safe at work. It helps workers avoid quick injuries and health problems that last a long time.
Chemical Hazards and Injuries
Types of Chemical Hazards
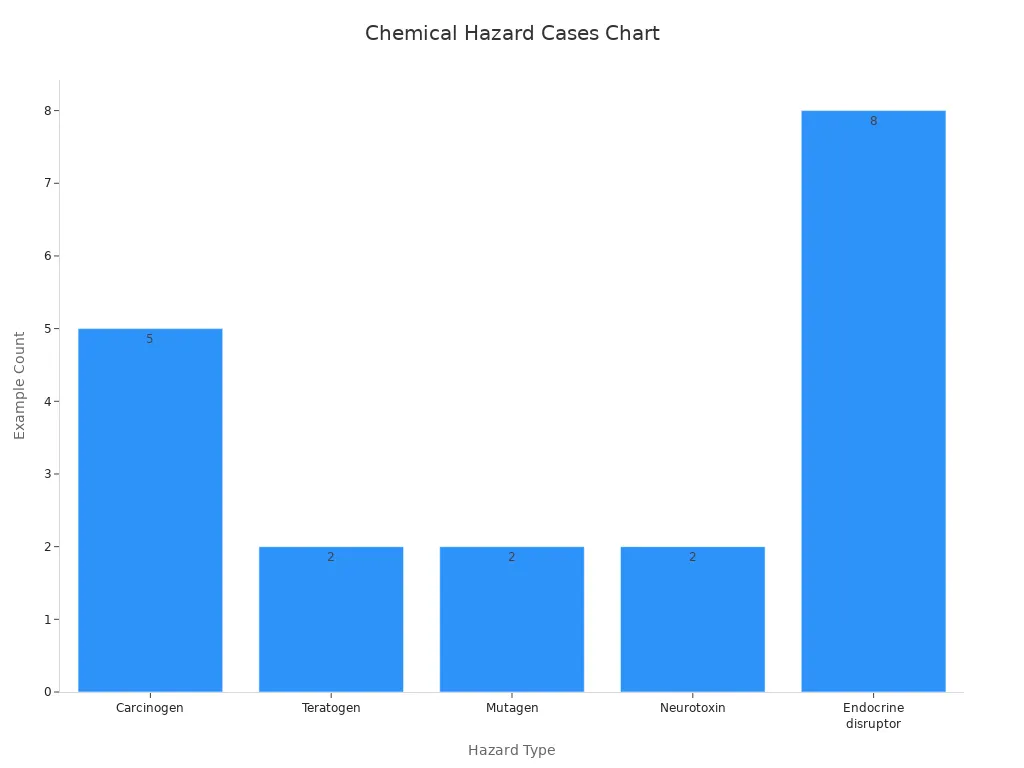
Many jobs have different chemical hazards. These hazards can hurt the body in many ways. Chemicals can be gases, liquids, or solids. Workers often use cleaning agents, solvents, and acids. Some chemicals can cause cancer or birth defects. Others can harm nerves or change DNA.
|
Type of Chemical Hazard |
Description |
Examples |
|---|---|---|
|
Carcinogen |
Agents that can cause cancer alone or with others. |
Formaldehyde, asbestos, radon, vinyl chloride, tobacco |
|
Teratogen |
Substances that cause birth defects in embryos. |
Alcohol, cigarette smoke |
|
Mutagen |
Materials that make changes in DNA. |
Radioactive substances (radon, nuclear fuel/waste), nitrous acid |
|
Neurotoxin |
Substances that hurt the nervous system. |
Lead, mercury |
|
Endocrine disruptor |
Chemicals that mess with hormones and cause health problems. |
Pharmaceuticals, dioxins, arsenic, PCBs, DDT, PFAS, phthalates, BPA |
Note: Chemical hazards also include welding vapors, gases like ammonia or carbon monoxide, and flammable things like gasoline or solvents.
A recent study found the most common chemical exposures for U.S. workers:
• Cleaning and antimicrobial agents (14.7%)
• Engine emissions (12.8%)
• Organic solvents (12.1%)
• Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (10.1%)
• Diesel engine emissions (8.3%)
These exposures often affect some groups more. People with less education, foreign-born workers, and males are at higher risk.
Common Hand Injuries
Chemical hazards can cause many hand injuries. Burns are very common. Strong acids or bases can burn skin fast. Some chemicals cause blisters, redness, or swelling. If you touch chemicals for a long time, your skin can get dry, cracked, or have rashes. Sometimes, chemicals go through the skin and hurt nerves or organs.
Workers can also have allergic reactions. Some chemicals make skin itch or break out in hives. If you touch chemicals a lot, your skin can get more sensitive. Over time, this can cause skin problems that last. In rare cases, chemicals can badly damage tissue or leave scars forever.
• Tip: The right gloves and following safety rules help stop these injuries.
How Chemical Resistant Gloves Work
Glove Materials
The material of a glove is important for protection. Each type of glove material has special strengths. Nitrile, latex, neoprene, and PVC are used a lot. Nitrile gloves, like ChemTuff™ Disposable Nitrile Gloves, protect well from many chemicals. They also do not cause latex allergies. Latex gloves are soft and comfortable. But they do not stop every chemical. Neoprene gloves work well against acids and oils. PVC gloves are good for some solvents and cleaning products.
Scientists test glove materials in different ways. They check how chemicals move through the glove. They look at three things: permeation, penetration, and degradation. Permeation is when chemicals pass through the glove’s tiny parts. Penetration is when chemicals get in through holes or cracks. Degradation is when the glove changes, like swelling or fading.
|
Aspect |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Permeation |
Chemicals move through the glove material at a tiny level. |
|
Penetration |
Chemicals get through holes or weak spots in the glove. |
|
Degradation |
The glove changes shape, colour, or strength after chemical contact. |
Labs test how long it takes for chemicals to get through gloves. This is called breakthrough time. Gloves are rated from Level 1 to Level 6. Higher levels mean better protection. Gloves are also sorted into Type A, B, or C. Type A gloves protect from more chemicals for longer.
Protective Features
Some gloves have special features to keep hands safe. Many gloves have textured fingers for a better grip. Some have beaded cuffs to stop tearing and make them easy to take off. Ambidextrous gloves fit both hands. This saves time and cuts down on waste.
Certifications show if gloves meet safety rules. The EN374 standard checks if gloves block chemicals and germs. Labs test gloves for leaks with air and water. They also check if gloves stop viruses and blood-borne germs. Gloves that pass get special marks on their boxes.
Other tests check how fast chemicals go through the glove and how much damage they cause. These tests help workers pick the best glove for each job. Manufacturers give charts that match glove materials to certain chemicals. This helps people choose gloves that protect them the best.
Tip: Always look for certifications and test results before picking gloves for chemical jobs.
Choosing the Right Chemical Resistant Gloves
Selection Factors
Picking the right Chemical Resistant Gloves keeps workers safe from chemicals. There are many things to think about when choosing gloves for a job. One glove cannot stop every chemical. Workers need to use gloves that match the chemical and the job.
-
Chemical Compatibility:
Each glove material works best with certain chemicals. Nitrile, neoprene, butyl rubber, and PVC all protect against different dangers. For example, nitrile gloves work well against oils and many solvents. Workers should look at chemical resistance charts from glove companies before picking gloves. -
Breakthrough Time:
Breakthrough time shows how long a glove can stop a chemical before it gets through. Thicker gloves usually last longer. Tests like EN 16523-1 measure this time in minutes. Gloves with longer breakthrough times keep hands safer. -
Glove Thickness and Durability:
Thicker gloves often protect better, but can make it harder to feel things. Workers must find a balance between safety and moving their hands easily. Gloves should not tear or stretch too much during use. -
Fit and Comfort:
The right size glove keeps it from slipping or making the hands tired. Gloves with textured fingers help grip things, even if they are wet or oily. Features like sweat resistance and a good shape help workers wear gloves longer. -
Certifications and Manufacturer Guides:
Certified gloves meet tough safety rules. Workers should look for marks like EN 374 or ASTM D6319. Manufacturer guides and chemical charts help people pick the right glove for each chemical. -
Other Features:
Some gloves give extra safety, like cut or heat resistance. Workers should check their gloves before using them and get new ones if they are damaged. -
Tip: Always check the risks for each job. Real work can be different from lab tests.
INTCO’s ChemTuff™ Disposable Nitrile Gloves are a top choice. These gloves use strong nitrile that blocks many chemicals. ChemTuff™ gloves are 60% smoother than regular nitrile gloves, so they are easy to put on and take off. They let workers feel what they are doing, which helps with careful tasks. The gloves do not have powder or latex, so they lower allergy risks. Their strong and stretchy design, with elongation up to 500% and strength of at least 14 MPa, means they do not rip easily. ChemTuff™ gloves also have a beaded cuff for strength and textured fingers for a better grip.
Safety Standards
Safety standards help workers know which Chemical Resistant Gloves really protect them. International rules test gloves for chemical safety, strength, and how well they work.
|
Standard |
Scope/Focus |
Key Safety Requirements |
|---|---|---|
|
Protective gloves against chemicals & microbes |
Tests for penetration, degradation, permeation; performance levels Type A (≥6 chemicals), B (≥3), C (≥1) |
|
|
EN 455 |
Medical gloves |
Physical properties, biological evaluation, freedom from holes, shelf life, endotoxin and protein limits |
|
ASTM D6319 |
Nitrile gloves (U.S.) |
Material-specific standards for nitrile gloves |
EN ISO 374 checks if gloves can stop chemicals and germs. Type B gloves, like ChemTuff™, must block at least three chemicals for 30 minutes each. EN 455 makes sure gloves are strong and safe for medical jobs. ASTM D6319 sets rules for nitrile gloves, like how strong and flexible they are.
ChemTuff™ Disposable Nitrile Gloves meet EN ISO374 Type B. These marks show that the gloves protect against chemical splashes and are strong. ChemTuff™ gloves also meet EN 455, so they are safe and work well in many jobs.
Note: Always look for these marks on glove boxes. Certified gloves help workers trust their safety.
Chemical Resistant Gloves keep hands safe from harmful chemicals at work. It is important for workers to know the dangers and pick the right gloves. Checking gloves often and taking care of them helps stop injuries. Certified gloves like ChemTuff™ Disposable Nitrile Gloves provide strong safety and are comfortable. Using the best gloves for each job helps everyone stay safer.
Remember: Wearing the right gloves really helps in dangerous places.
FAQ
What are chemical resistant gloves?
Chemical resistant gloves keep hands safe from chemicals. They make a shield that blocks liquids or solids from touching the skin. People wear these gloves in labs, factories, and other places with chemical dangers.
What materials make the best chemical resistant gloves?
Nitrile, neoprene, latex, and PVC are used to make these gloves. Nitrile is good for many chemicals and does not cause latex allergies. Each type of glove protects against different dangers.
What do safety certifications mean on glove packaging?
Safety certifications like EN ISO 374 or ASTM D6319 mean that gloves have passed tough tests. These marks show workers that the gloves protect them from chemicals and other risks.
What should workers check before using chemical resistant gloves?
Workers need to check for holes, rips, or weak spots before use. Clean and dry hands help gloves fit better. Checking gloves first keeps hands safe from chemicals.
What makes INTCO’s ChemTuff™ Disposable Nitrile Gloves a premium choice?
ChemTuff™ gloves use strong nitrile and have a smooth feel. They let workers feel what they touch and meet top safety rules. These gloves are comfy and work well for hard jobs.